Research Highlights
Research Highlights
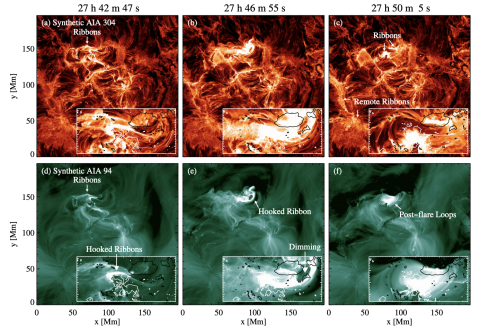
Eruption of a Magnetic Flux Rope in a Comprehensive Radiative Magnetohydrodynamic Simulation of flare-productive active regions
Feng Chen, Matthias Rempel, and Yuhong Fan present a radiative magnetohydrodynamic simulation that includes sufficiently realistic physics to allow for the synthesis of remote sensing observables that can be quantitatively compared with observations. The model helps to shed light on questions of where and when the a flux rope may form and how the magnetic structures in an eruption are related to observable emission properties.
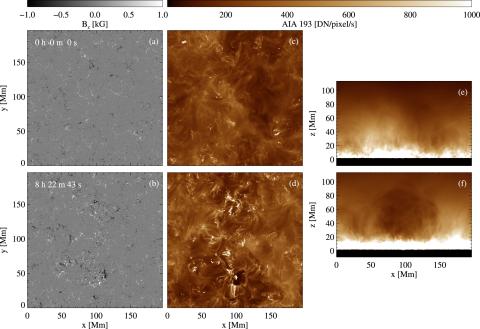
A Comprehensive Radiative Magnetohydrodynamics Simulation of Active Region Scale Flux Emergence from the Convection Zone to the Corona
Feng Chen, Matthias Rempel, and Yuhong Fan present a comprehensive radiative magnetohydrodynamic simulation of the quiet Sun and large solar active regions. This study provides a comprehensive view of the active region corona, such as coronal loops of various lengths and temperatures, mass circulation by evaporation and condensation, and eruptions from jets to large-scale mass ejections.
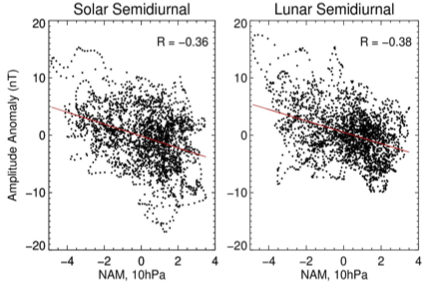
Impact of strong and weak stratospheric polar vortices on geomagnetic solar and lunar tides
N. M. Pedatella, et al. investigate the impact of strong and weak stratospheric polar vortices on geomagnetic semidiurnal solar and lunar tides during Northern Hemisphere (NH) winters using ground-based magnetic field observations at the Huancayo (-12.05° N, 284.67° E; magnetic latitude: -0.6° N) equatorial observatory.
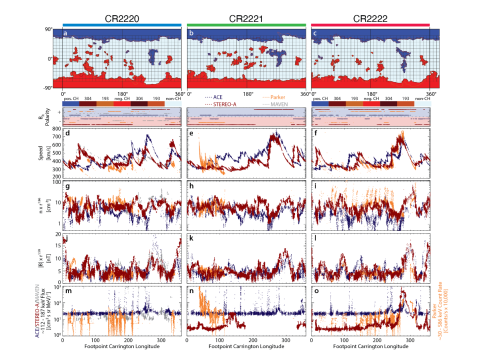
A Mosaic of the inner heliosphere:
Sarah E. Gibson, et al. provide an expansive mosaic of observations spanning from the Sun, through interplanetary space, to the magnetospheric response and subsequent effects on the ionosphere-thermosphere-mesosphere (ITM) system. To accomplish this, a diverse set of observational datasets are utilized and focused on two long-lived coronal holes and their varying impact in sculpting the heliosphere and driving of the magnetospheric system.
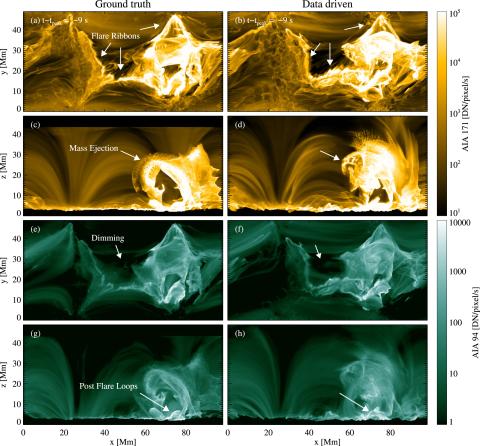
Data-driven Radiative Magnetohydrodynamics Simulations with the MURaM Code
Feng Chen, Mark C.M. Cheung, Matthias Rempel, and Georgios Chintzoglou present a method of conducting data-driven simulations of solar active regions and flux emergence with the MURaM radiative magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) code. This method helps to understand the evolution of magnetic field in a more realistic coronal environment and to link the magnetic structures to observable diagnostics.

Small-scale dynamos: From idealized models to solar and stellar applications
Matthias Rempel, Tanayveer Bhatia, Luis Bellot Rubio, and Maarit J. Korpi-Lagg review small-scale dynamo processes that are responsible for magnetic field generation on scales comparable to and smaller than the energy carrying scales of turbulence. We provide a review of critical observation of quiet Sun magnetism, which have provided strong support for the operation of a small-scale dynamo in the solar photosphere and convection zone.
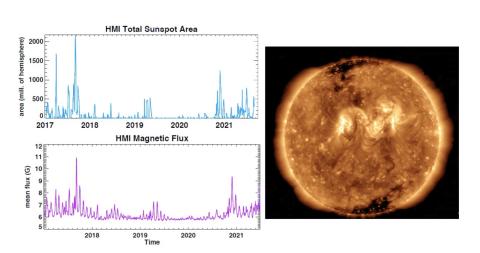
Whole Heliosphere and Planetary Interactions (WHPI): The Big Picture on Solar Cycle Minima
Sarah E. Gibson, et. al. discuss the Whole Heliosphere and Planetary Interactions (WHPI,) an international initiative to study the most recent solar minimum and its impact on the interconnected solar-heliospheric-planetary system by facilitating and encouraging interdisciplinary activities, placing it into the context of prior initiatives and describing the overall evolution of the system between 2018–2020.
Delineating the effect of upward propagating migrating solar tides with the TIEGCM-ICON
Astrid Maute, Jeffrey Forbes, Chihoko Cullens, and Thomas Immel use the thermosphere-ionosphere-electrodynamics general circulation model (TIEGCM) driven by observationally fitted tides via the Hough Mode Extension (HME) method to isolate the effect of the changing upward propagating tides on the dynamics, composition, and plasma distribution .
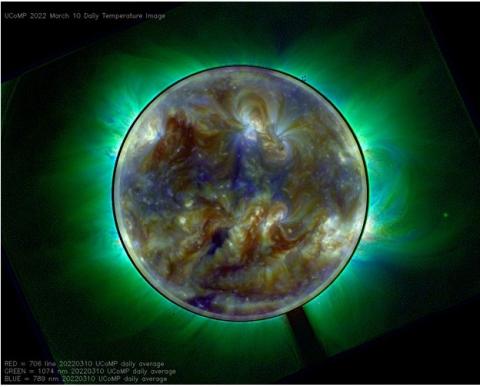
Coronal spectral diagnostics: The Coronal Solar Magnetic Observatory (COSMO)
Sarah E. Gibson et. al. emphasize the need of understanding and predicting the major phenomena taking place in the solar corona, such as flares and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), the heating and evolution of the solar atmosphere, and the acceleration of the solar wind, are fundamental challenges to predict our own star. These challenges are related to the solar magnetism and to the physical properties of solar plasma.