Geospace Dynamics Constellation Example
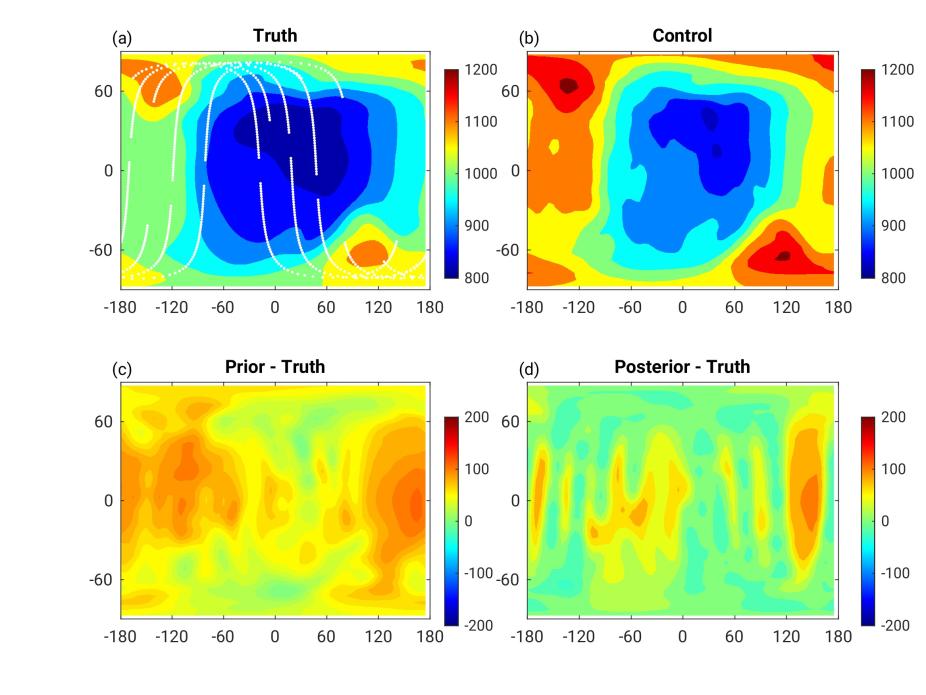
The longitude-latitude distribution of neutral temperature from the pressure level 19 that corresponds to about 350 km altitude at UT 01 on 17 March 2013 from OSSE5. (a) True distribution from the nature run overlaid with GDC observation locations indicated by white dots. (b) Mean distribution from the control ensemble simulation with no DA. (c) Differences between the experiment result and truth before DA. (d) Differences between the experiment result and truth after DA.
Earth and Space Science: Observing System Simulation Experiments (OSSEs) provide an effective way to evaluate the impact of assimilating data from a specific observing system on hindcasting, nowcasting, and forecasting of environmental systems. The NSF NCAR's Data Assimilation Research Testbed/Thermosphere-Ionosphere-Electrodynamics General Circulation Model (DART/TIEGCM) tool, to be hosted at the NASA Community Coordinated Modeling Center (CCMC), serves as a valuable and accessible community resource for quantitatively evaluating the impact of observations from both current and future ionosphere-thermosphere (IT) observing systems.
Chih-Ting Hsu, et al. in this study demonstrate the utility of DART/TIEGCM as an IT OSSE tool, using synthetic observations simulated using a currently planned NASA Geospace Dynamics Constellation (GDC) observing system design. Five sets of OSSEs are carried out to compare the effects of assimilating various combinations of prospective GDC observations (e.g., neutral temperature, neutral wind, neutral composition, atomic oxygen ion density, and ion and electron temperature) during a major geomagnetic storm period of the St Patrick's Day Storm on March 17, 2013. These OSSEs indicate the benefits of coupled IT data assimilation approaches implemented in DART/TIEGCM to maximize the impact of multi-parameter IT observations, such as those expected from the GDC mission. Although more work is required to draw any definitive conclusion on the GDC data impact, the study provides an illustrative example of how the DART/TIEGCM community tool can be used to evaluate observational impacts of planned or existing missions for geospace research and applications.