Research Highlights
Research Highlights

Near-Ultraviolet Spectropolarimetry as a tracer of Magnetic Markers of Flux Rope Formation
Authors D. Afonso Delgado, R. Centeno, R. Casini, and M. Rempel investigate the suitability of the combined spectral windows of Mg II h and k and the Fe II lines around 261 nm as magnetic markers of filament formation.

Polarization Diagnostics Applied to Coronal Mass Ejections and the Background Solar Wind
Sarah E Gibson, Craig E. DeForest, Curt A. de Koning, Steven R. Cranmer, Yuhong Fan, Huw Morgan, Elena Provornikova, Anna Malanushenko, and David Webb use PUNCH polarization data to analyze individual lines of sight to three-dimensional models of coronal mass ejections (CMEs), allowing consideration of how accurately polarization properties of the transient and quiescent solar wind are diagnosed.

Quantifying Day-To-Day Variability of the Ionosphere and Thermosphere Induced by Upward Propagating Migrating Diurnal and Semidiurnal Tides
Tianyang Hu, Liying Qian, Nicholas Pedatella, Wenbin Wang, and Quan Gan use a whole atmosphere model, the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model with thermosphere‐ionosphere eXtension (WACCM-X), to investigate the role of upward propagating migrating diurnal and semidiurnal tides on the day-to-day variability in the I-T system.

Advancing Heliophysics and Space Weather Modeling through Open Science
HAO first author, Michael Wiltberger, et. al. highlight a community-wide effort to understand how “open science” practices can better support research and forecasting in heliophysics and space weather.

Refining the Magnetic Field Estimate for the Solar Polar Region
Bryan Yamashiro, Xudong Sun, Ivan Milic, Carlos Quintero Noda, Jiayi Liu, Adur Pastor Yabar, Rebecca Centeno, Milan Gosic, and Kai Yang analyze a raster map of the southern polar region taken by the Hinode Spectro-Polarimeter, utilizing the Stokes Inversion based on Response functions code. The inversions provide height-dependent vector magnetic field maps between optical depths log(tau) = -2 and 0.
MHD-tachocline-model solutions of magnetic vectors
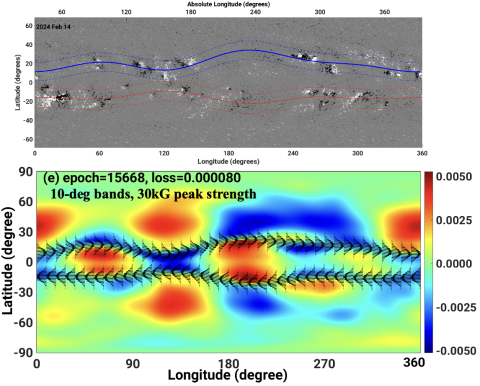
S. Chatterjee and M. Dikpati develop PINNBARDS, a novel Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN)-Based AR Distribution Simulator, that uses observational toroids and MHD-SWT equations to derive initial state-vector. This framework provides the first plausible method for reconstructing state-vectors for hidden tachocline magnetic structures from surface patterns; this could potentially lead to accurate prediction of flare-producing AR-emergence weeks ahead.
A Multi-layer Magnetohydrodynamic Shallow-water Model of The Solar Tachocline: Equilibrium Shape and Thickness
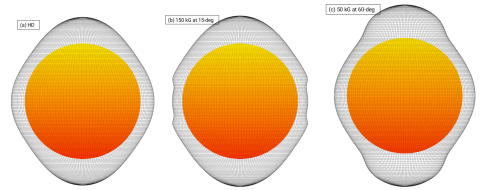
M. Dikpati and P. A. Gilman build a multi-layer MHD shallow-water model to study the thickness and shape of a the solar tachocline allowing them to include characteristics of both the overshoot and the radiative parts of the tachocline.
Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere (PUNCH)
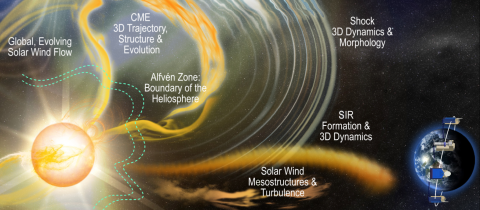
Sarah Gibson, et. al. present the two science objectives behind the Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere (PUNCH) mission: (1) understand how coronal structures become the ambient solar wind, and (2) understand the dynamic evolution of transient structures, such as coronal mass ejections, in the young solar wind. PUNCH is a NASA Small Explorer launched in March of 2025 and began science operations in June of 2025.
Efficiency of Electromagnetic Energy Transfer from Solar Wind to Ionosphere through Magnetospheric Ultra-Low Frequency Waves
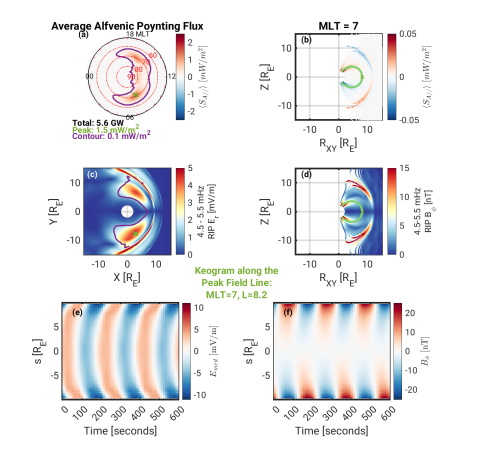
Dong Lin, Michael Hartinger, William Lotko, Wenbin Wang, Xueling Shi, Bharat Kunduri, Viacheslav Merkin, Kareem Sorathia, Kevin Pham, and Michael Wiltberger perform idealized numerical experiments to investigate the electromagnetic energy flow in response to undulating solar wind. The theoretical study provides new understanding of the significance of the electromagnetic energy flow and its dependence on different parameters.