This study (Journal of Geophysical Research–Space Physics) investigates the impact of assimilating electron density profiles from the Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere, and Climate-2 (COSMIC-2) mission in a whole atmosphere data assimilation system. The observations are assimilated into the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model with thermosphere-ionosphere eXtension (WACCMX) using the Data Assimilation Research Testbed (DART) ensemble adjustment Kalman filter. Assimilation of the COSMIC-2 electron density profiles during the evaluation time period of 25–30 April 2020 leads to improvement in both the 1 hr forecast and analysis electron densities in WACCMX + DART. Compared to a control experiment that does not assimilate COSMIC-2 observations, the assimilation of the COSMIC-2 electron density profiles reduces the 1 hr forecast root mean square error (RMSE) and bias with respect to COSMIC-2 observations at 300 km by 6.76% and 24.91%, respectively. Assimilation of the COSMIC-2 electron density profiles does not significantly influence the RMSE and bias with respect to ground-based Global Navigation Satellite System vertical total electron content observations. The equatorial vertical plasma drift velocity in WACCMX + DART is changed by ±5–10 ms−1 due to the assimilation of the COSMIC-2 electron density profiles, indicating that the model representation of the electrodynamics of the low latitude ionosphere are significantly impacted by the assimilation of COSMIC-2 observations.
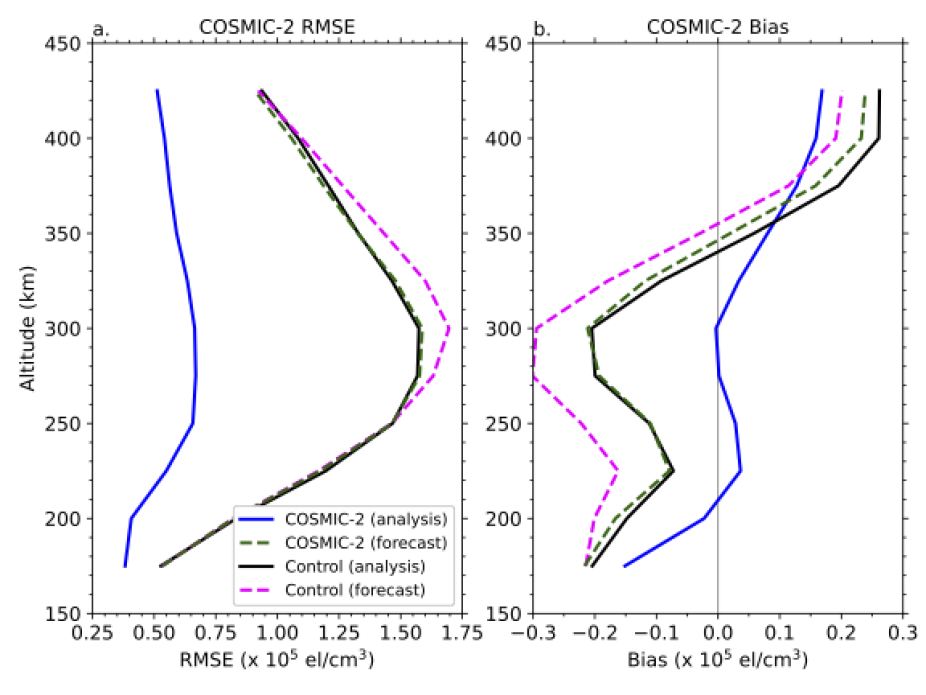
WACCMX+DART analysis and 1 hr forecast (a) root mean square error and (b) bias relative to COSMIC-2 electron density observations. Results are for 25-30 April 2020, and all longitudes between 60S to 60N. The COSMIC-2 experiment assimilates COSMIC 2 electron density profile observations, and the Control experiment does not. The results demonstrate the positive impact of assimilating the COSMIC-2 observations on the analysis and short-term (1 hr) forecasts.