Publication: JR Space Physics; Authors: Xuguang Cai, Wenbin Wang, Alan Burns, Liying Qian, Richard W. Eastes
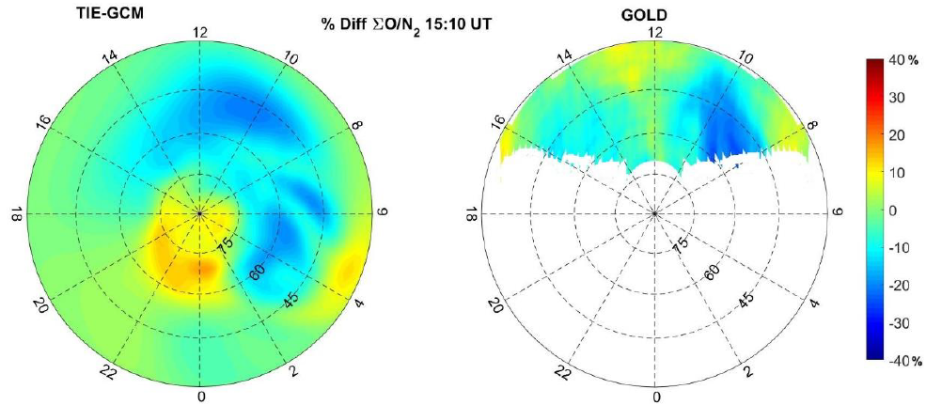
The polar view of the percentage difference of simulated ∑O/N2 and GOLD observed ∑O/N2 between DOY 111 and 110 at 15:10 UT in 2019. The perimeter latitude is 30°N
Numerical simulations using the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) thermosphere-ionosphere-electrodynamics general circulation model (TIE-GCM) are performed to elucidate the effects of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) on the middle thermosphere composition during a “geomagnetically quiet” period from the day of year (DOY) 110-111 in 2019 (when the Auroral electrojet (AE) index never exceeded 300 nT and the Kp never exceeded 2). In particular, this paper aims to examine how the Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk (GOLD) mission observed daytime thermospheric O and N2 column density ratio (∑O/N2) depletion at mid-latitudes originated under such a “geomagnetically quiet” condition. A comparison of electric potential, Joule heating rate per unit mass, ion velocity, neutral temperature and winds in the middle thermosphere (∼160 km) between real IMF and without the IMF east-west component (By) indicates that a By dominant condition can enhance their strengths under this “geomagnetically quiet” condition. Consequently, ∑O/N2 depletion with a stronger magnitude (30% compared with ∼8% without By) and larger disturbed area was introduced in the post-midnight sector at high-latitudes due to strong and localized upwelling associated with the enhanced Joule heating rate per unit mass. The ∑O/N2 depletion was transported equatorward and corotated from local post-midnight to early morning, and was observed by GOLD at middle latitudes during daytime.