Research Highlights
Research Highlights
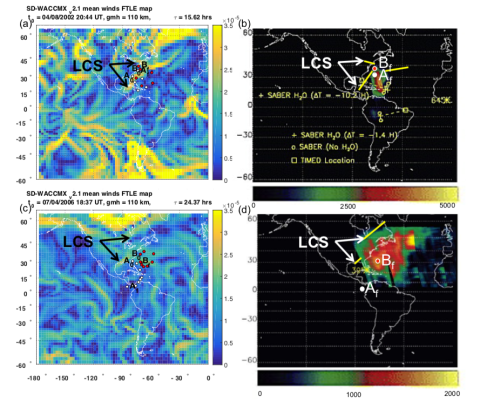
Lower thermospheric material transport via Lagrangian coherent structures
Lagrangian coherent structures (LCSs), indicating regions of material transport, are derived from models of the lower thermosphere for five space shuttle water vapor plume events. LCSs defined using flow fields from the Specified Dynamics version of the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model with thermosphere eXtension (SD-WACCMX) are compared to global ultraviolet imager (GUVI) observations of water vapor documented in the literature.
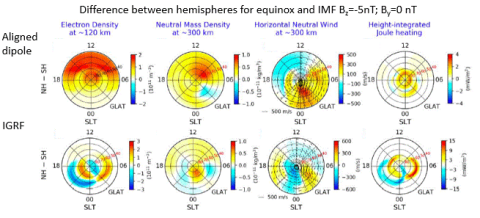
Impacts of Different Causes on the Inter–Hemispheric Asymmetry of Ionosphere–Thermosphere System at Mid– and High–Latitudes: GITM Simulations
There are significant differences between the Earth’s two hemispheres such as the Earth's magnetic field and the intensity of solar radiation due to Earth's tilt of the rotation axis with respect to the Sun. Understanding the impact and therefore the importance of these asymmetries on the mid- and high-latitude upper atmosphere is a challenge in the geospace community.
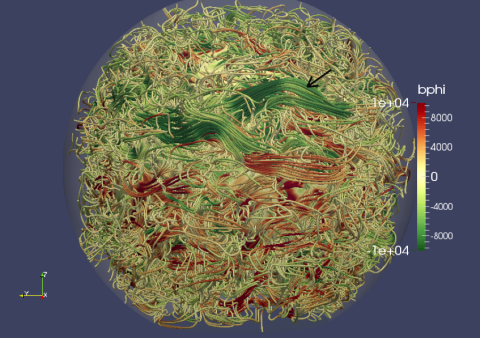
Magnetic fields in the solar convection zone (major update)
It has been a prevailing picture that active regions on the solar surface originate from a strong toroidal magnetic field stored in the overshoot region at the base of the solar convection zone, generated by a deep seated solar dynamo mechanism. This article reviews the studies in regard to how the toroidal magnetic field can destabilize and rise through the convection zone to form the observed solar active regions at the surface.
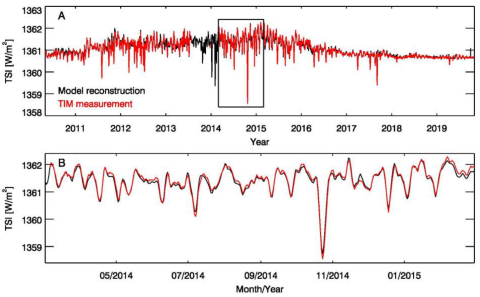
The Dimmest State of the Sun
How the solar electromagnetic energy entering the Earth’s atmosphere varied since pre-industrial times is an important consideration in the climate change debate.
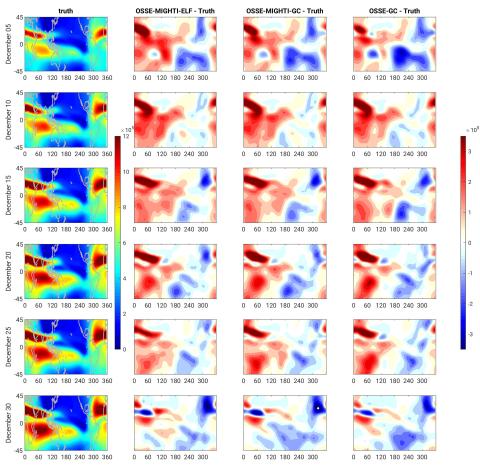
Impact of Thermospheric Wind Data Assimilation on Ionospheric Electrodynamics using a Coupled Whole Atmosphere Data Assimilation System
The upward plasma drift and equatorial ionization anomaly (EIA) in the Earth's ionosphere are strongly influenced by the zonal electric field, which is generated by the wind dynamo. Specification and forecasting of thermospheric winds thus plays an important role in ionospheric weather prediction.
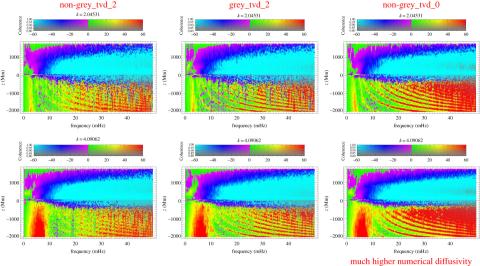
Acoustic-gravity wave propagation characteristics in three-dimensional radiation hydrodynamic simulations of the solar atmosphere
There has been tremendous progress in the degree of realism of three-dimensional radiation magneto-hydrodynamic simulations of the solar atmosphere in the past decades.
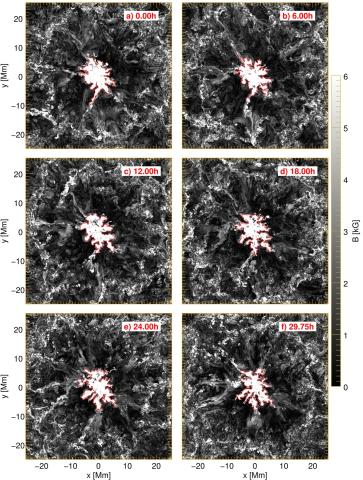
On the (In)stability of Sunspots
The stability of sunspots is one of the long-standing unsolved puzzles in the field of solar magnetism and the solar cycle. The thermal and magnetic structure of the sunspot beneath the solar surface is not accessible through observations, thus processes in these regions that contribute to the decay of sunspots can only be studied through theoretical and numerical studies.
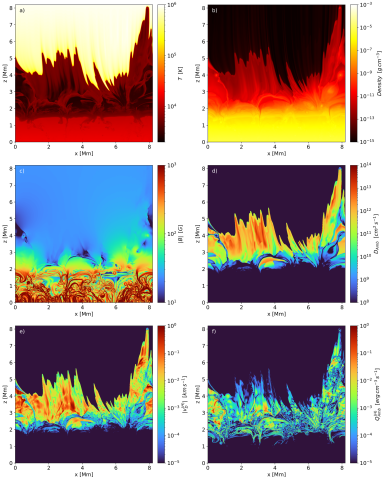
Efficient numerical treatment of ambipolar and Hall drift as hyperbolic system
Partially ionized plasmas, such as the solar chromosphere, require a generalized Ohm's law including the effects of ambipolar and Hall drift. While both describe transport processes that arise from the multifluid equations and are therefore of hyperbolic nature, they are often incorporated in models as a diffusive, i.e. parabolic process. While the formulation as such is easy to include in standard MHD models, the resulting diffusive time-step constraints do require often a computationally more expensive implicit treatment or super-time-stepping approaches.
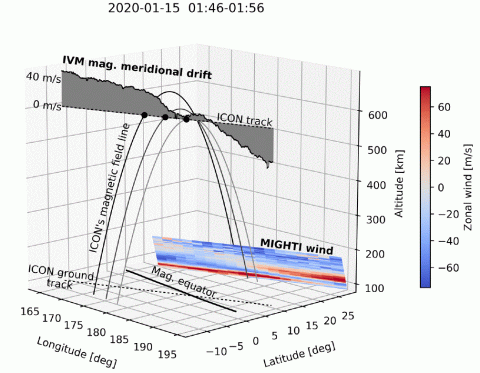
Control of ionospheric plasma velocities by thermospheric winds
Earth’s equatorial ionosphere exhibits significant and unpredictable day-to-day variations in density and morphology. The NASA Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) makes the first coordinated space-based observations of the wind-driven dynamo and the plasma state to understand the relation of the plasma environment to the thermospheric weather below.