Research Highlights
Research Highlights
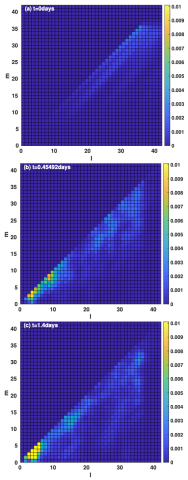
Simulating Solar Near-surface Rossby Waves By Inverse-cascade From Supergranule Energy
M. Dikpati, P. A. Gilman, G. A. Guerrero, A. G. Kosovichev, S. W. McIntosh, K. R. Sreenivasan, J. Warnecke, T. V. Zaqarashvili show that Rossby waves in the supergranule layer can be excited by an inverse cascade of kinetic energy from the nearly horizontal motions in supergranules. They illustrate how this excitation occurs using a hydrodynamic shallow-water model for a 3D thin rotating spherical shell.
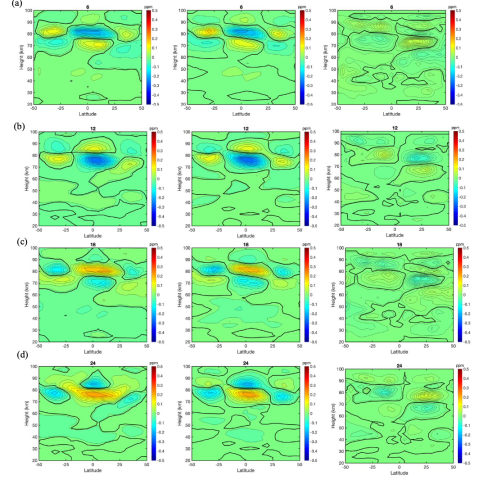
A Lagrangian Study of Tidal Advection of Mesospheric Water Vapor
N. Koushik, J. Oberheide, and N. M. Pedatella study the sources of diurnal variability of water vapor in the mesosphere with the help of the specified dynamics configuration of the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model with thermosphere-ionosphere eXtension (SD-WACCM-X) for typical equinox conditions during the solar minimum year 2009. Special emphasis is given to the advective transport by the migrating diurnal tide and its impact on the mean water vapor in the mesosphere.
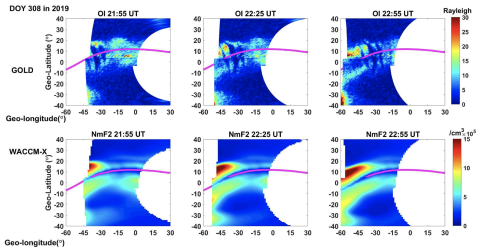
Investigation of the Post-Sunset Extra Electron Density Peak Poleward of the Equatorial Ionization Anomaly Southern Crest
Xuguang Cai, Liying Qian, Wenbin Wang, Joseph M. McInerney, Han-Li Liu, and Richard W. Eastes reveal that the Global-scale observation of limb and disk mission observed an extra electron density (Ne) peak after sunset at approximately 30°S near 40°W on 4 November 2019, which is poleward and immediately next to the southern equatorial ionization anomaly (EIA) crest.
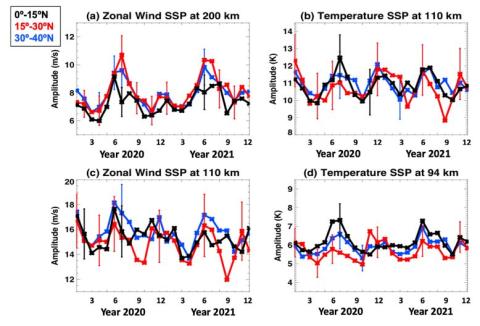
Seasonal Variations of Small-Scale Waves observed by ICON-MIGHTI
C. Y. Cullens, S. England, T. J. Immel, A. Maute, B. J. Harding, C. Triplett, J.J. Makela, et al. analyze the seasonal variations of small-scale perturbations between 90 km to 250 km using temperature and winds measurements made by the Michelson Interferometer for Global High-Resolution Thermospheric Imaging (MIGHTI) instrument onboard the Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite in the latitude range of 0°-40° N in the year of 2020-2021.
Assessing the Demographics of the 2021 and 2022 CEDAR Workshop
McArthur Jones and Astrid Maute report the demographic information obtained for the 2021 virtual workshop and 2022 in-person workshop. In general, the demographics of CEDAR are consistent with those in the broader science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields, that is, most participants identify as male, White, and/ or Asian/Middle Eastern.
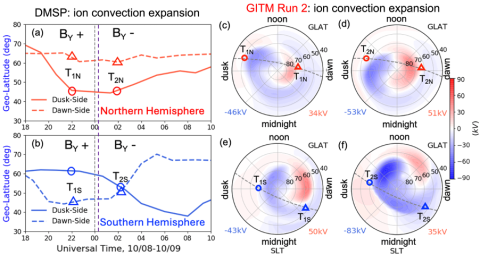
Inter-Hemispheric Asymmetries in the High-Latitude Electrodynamic Forcing and the Thermosphere During the October 8-9, 2012 Geomagnetic Storm: An Integrated Data-Model Investigation
Y. Hong, Y. Deng, Q. Zhu, A. Maute, M. Hairston, C. Sheng, D. Welling, R. Lopez utilize field-aligned currents (FACs) obtained from the Active Magnetosphere and Planetary Electrodynamics Response Experiment data set to specify the high-latitude electric potential in the Global Ionosphere and Thermosphere Model (GITM) to examine the IHAs in the IT system during the 8-9 October 2012 storm.
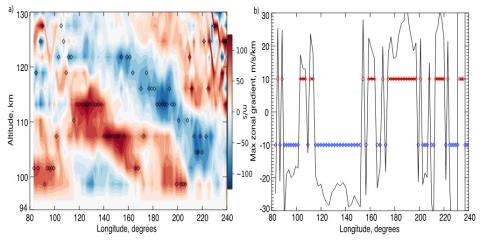
Horizontal wind shears in the lower thermosphere observed by ICON
S. L. England, C. R. Englert, B. J. Harding, C. C. Triplett, K. Marr, J.M. Harlander, G.R. Swenson, A. Maute, and T. Immel make observations from the MIGHTI instrument on board the Ionospheric Connection Explorer are analyzed to determine the maximum wind shear in the 95-120 km region during the day time. The strong shear occurrence, horizontal scale and underlying organization is examined.
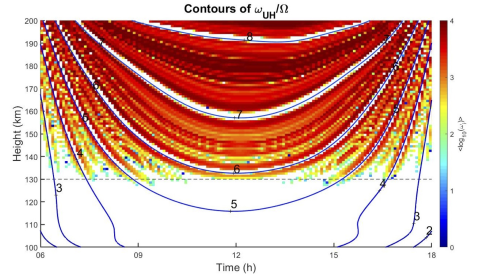
The photoelectron driven upper hybrid instability as the cause of 150 km echoes
Nicholas Pedatella discusses strong, unexplained echoes returning from altitudes of 130–170 km in the atmosphere; how all radars work by reflecting radio waves off a target and measuring the returned signal. This region (130–170 km) in the upper atmosphere is likely to create and maintain a specific set of plasma waves that act as a coherent structure for radar measurements.
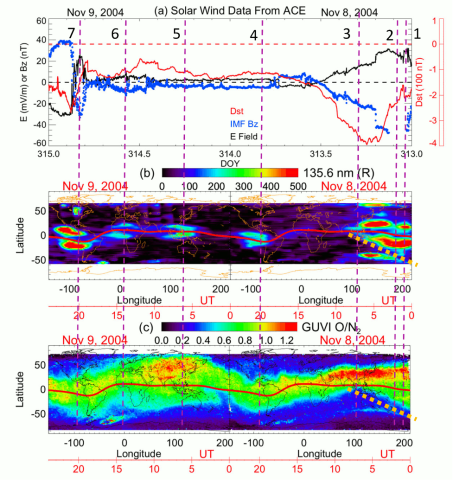
FUV Observations of Variations in Thermospheric Composition and Topside Ionospheric Density During the November 2004 Magnetic Superstorm
Y. Zhang, L. Paxton, C. Huang, and W. Wang, observe that the 135.6 nm radiances clearly showed a signature of ionospheric equatorial arcs and their variations during the November 2004 magnetic superstorm. When an intense eastward Interplanetary Electric Field (IEF) occurred, the dayside equatorial arcs were enhanced and their latitude separation increased.