Research Highlights
Research Highlights
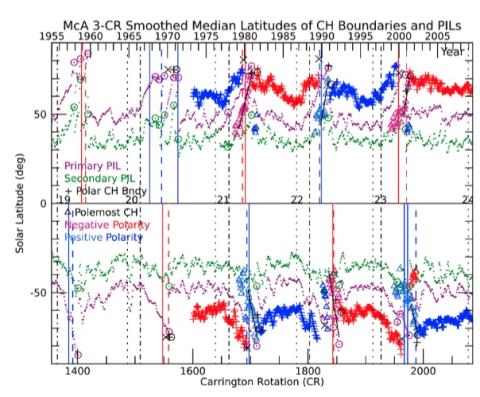
The Polar Field Reversal Process over Five Solar Cycles
D. F. Webb, B. A. Emery, S. E. Gibson, I. M. Hewins, R. H. McFadden , T. A. Kuchar examine the process during which the solar magnetic field reverses polarity around solar maximum using the McIntosh Archive (McA) of solar synoptic maps over five consecutive solar cycles, SCs 19-23 or from 1955 to 2009. This data set permits us to track features such as filaments, polarity inversion lines (PILs), coronal hole (CH) boundaries and sunspots over many consecutive Carrington rotations and solar cycles.
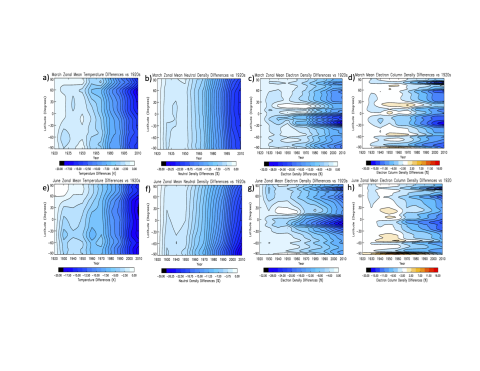
Climate Change in the Thermosphere and Ionosphere From the Early Twentieth Century to Early Twenty‐First Century Simulated by the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model—eXtended
Authors Joseph McInerney, Liying Qian, Han-Li Liu, Stanley Solomon, and Susan Nossal decided to apply the WACCM-X climate model to the upper atmosphere for the decades from the 1920s to 2010s. This type of modeling application will be useful to predict what will happen in the century ahead as greenhouse gases increase and humans make efforts to reverse the increase.
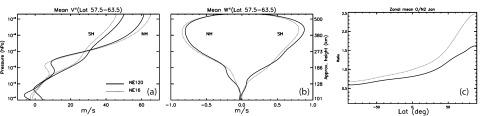
Impacts of gravity waves on the thermospheric circulation and composition
Hanli Liu, Peter Lauritzen, and Francis Vitt use the high-resolution whole atmosphere model to study small-scale wave propagation from the lower atmosphere into the thermosphere. Using this high-resolution model, which can partially resolve the small-scale waves, they can directly quantify the force exerted by these waves on the general circulation in the thermosphere.
Mapping the Sun’s Alfvén Surface with PUNCH
Steven Cranmer, Rohit Chhiber, Chris Gilly, Iver Cairns, Robin Colaninno, David McComas, Nour Raouafi, Arcadi Usmanov, Sarah Gibson, Craig DeForest review the properties of Alfvén surface and discuss its importance in models of solar wind acceleration, angular momentum transport, MHD waves and turbulence, and the geometry of closed coronal loops. Simulations results and data analysis techniques are used to determine the location of the Alfvén surface.
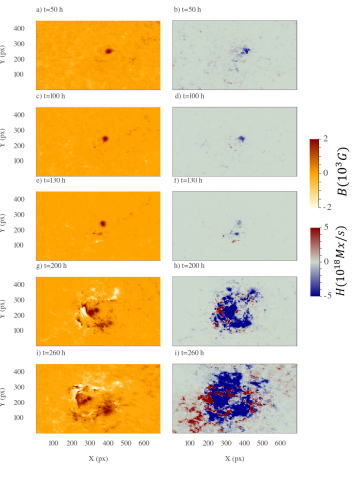
Deciphering Pre-solar-storm Features Of September-2017 Storm From Global And Local Dynamics
B. Raphaldini, M. Dikpati, A. A. Norton, A. S. W. Teruya, S. W. McIntosh, C. B. Prior, and D. MacTaggart investigate how global toroid patterns and local magnetic field topology of solar active region AR12673 together can hindcast occurrence of the biggest X-flare of cycle 24. We infer that minimum-phase storms can be forecast only hours ahead, while flare-prone active regions in peak-phase can be anticipated at least a month ahead from global toroid patterns.
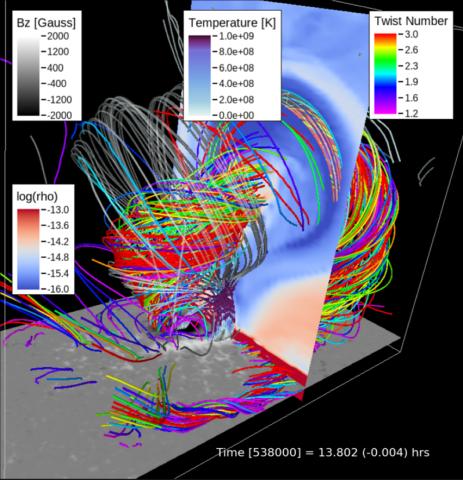
Comprehensive Radiative MHD Simulations of Eruptive Flares above Collisional Polarity Inversion Lines
Matthias Rempel, Georgios Chintzoglou, Mark C. M. Cheung, Yuhong Fan, and Lucia Kleint—Solar flares are bursts of high-energy radiation that are associated with sunspots. NOVA highlights this newly published research that uses models to study what happens when sunspots collide and under what conditions these collisions cause solar flares.
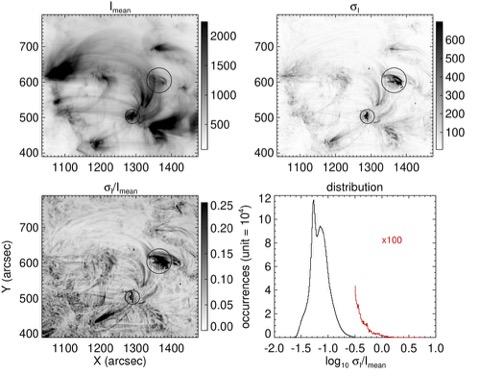
Steadiness of coronal heating
Philip Judge evaluates images from the Solar Orbiter spacecraft to determine the steadiness of coronal heating. The widely-held belief that the outer atmosphere of the Sun is in a continuous state of magnetic turmoil is pitted against the EUI data with very illuminating results.
My Rewarding Life in Science
This fascinating memoir covers the scientific life of Dr. Andrew Skumanich, starting with his family’s background and their immigration to the US. It continues with Andy's childhood, early education, his influential introduction to science, and finally his illuminating career, which started at Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory in the 1950s and then continued in solar physics at the High Altitude Observatory (National Center for Atmospheric Research).
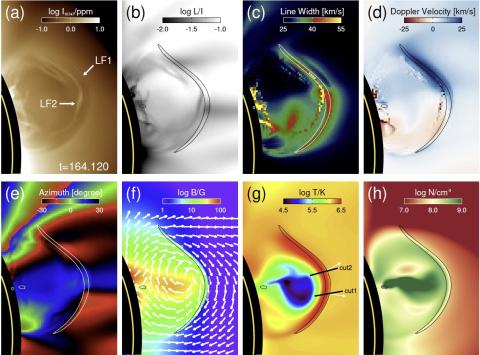
Magnetic field and plasma diagnostics for solar coronal mass ejections: A case study using the forward modeling approach
X. Liu, H. Tian, T. Toeroek, S. Gibson, Z. Yang, W. Li, and T. Samanta show results that the COronal Solar Magnetism Observatory (COSMO) Large Coronagraph (LC) can provide magnetic field measurements of CME progenitors with a high spatial resolution (2′′ pixels). By using a worse resolution (6′′ pixels), the COSMO LC observation may also be used to qualitatively study the evolution of magnetic field during the CME eruption.