Research Highlights
Research Highlights

Investigation of the physical mechanism of the formation and evolution of equatorial plasma bubbles during a moderate storm on September 17, 2021
Kun Wu, Liying Qian, Wenbin Wang, Xuguang Cai, Joseph M. Mclnerney investigate in detail the occurrence and evolution of ionospheric equatorial plasma bubbles (EPBs) during a moderate storm on September 17th, 2021, using Global-scale Observation of the Limb and Disk (GOLD) observations and Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model-eXtended (WACCM-X) simulations.
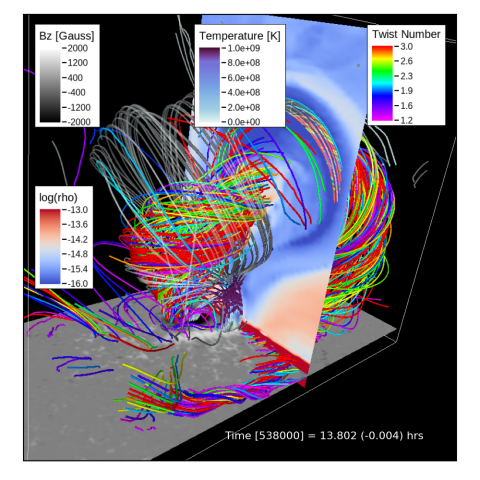
Comprehensive Radiative MHD Simulations of Eruptive Flares above Collisional Polarity Inversion Lines
Matthias Rempel, Georgios Chintzoglou, Mark C. M. Cheung, Yuhong Fan, and Lucia Kleint present a new simulation setup using the MURaM radiative Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) code that allows to study the formation of collisional polarity inversion lines (cPILs) in the photosphere and the coronal response including flares. In this scheme we start with a bipolar sunspot configuration and set the spots on collision course by imposing the appropriate velocity field at the footpoints in the subphotospheric boundary.
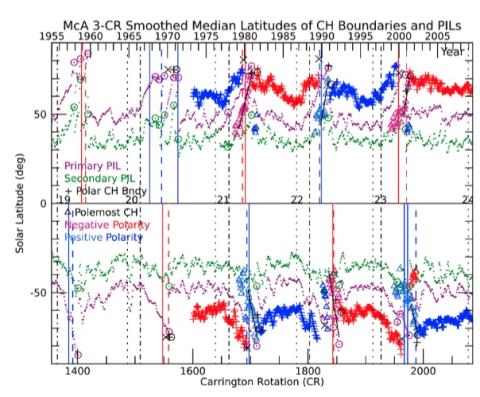
The Polar Field Reversal Process over Five Solar Cycles
D. F. Webb, B. A. Emery, S. E. Gibson, I. M. Hewins, R. H. McFadden , T. A. Kuchar examine the process during which the solar magnetic field reverses polarity around solar maximum using the McIntosh Archive (McA) of solar synoptic maps over five consecutive solar cycles, SCs 19-23 or from 1955 to 2009. This data set permits us to track features such as filaments, polarity inversion lines (PILs), coronal hole (CH) boundaries and sunspots over many consecutive Carrington rotations and solar cycles.
Quasi 6-Day Planetary Wave Oscillations in Equatorial Plasma Irregularities
N. M. Pedatella, E. Aa, and A. Maute explore the influence of atmospheric planetary waves on the occurrence of irregularities in the low latitude ionosphere is investigated using Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model with thermosphere-ionosphere eXtension (WACCM-X) simulations and Global Observations of the Limb and Disk (GOLD) observations.
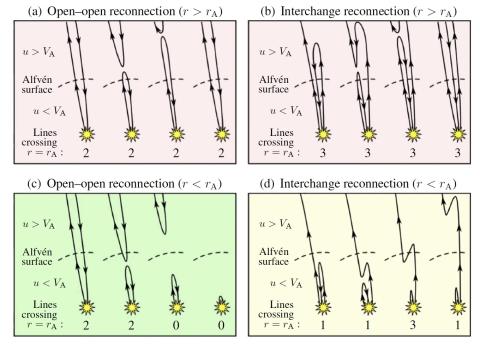
The Sun's Alfvén Surface: Recent Insights and Prospects for the Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere (PUNCH)
Sarah Gibson et al., review the properties of an irregularly shaped “Alfvén surface” surface and discuss its importance in models of solar wind acceleration, angular momentum transport, MHD waves and turbulence, and the geometry of closed coronal loops. We also review the results of simulations and data analysis techniques that aim to determine the location of the Alfvén surface.
Inflows towards Bipolar Magnetic Active Regions and Their Nonlinear Impact on a Three-Dimensional Babcock-Leighton Solar Dynamo Model
Kinfe Teweldebirhan, Mark Miesch, and Sarah Gibson investigate the role and impact of converging flows toward Bipolar Magnetic Regions (BMR inflows) on the Sun’s global solar dynamo. These flows are large-scale physical phenomena that have been observed and so should be included in any comprehensive solar dynamo model.
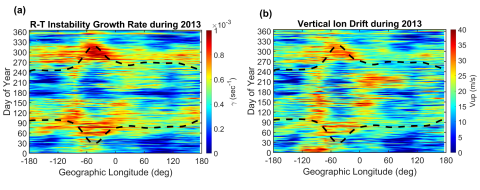
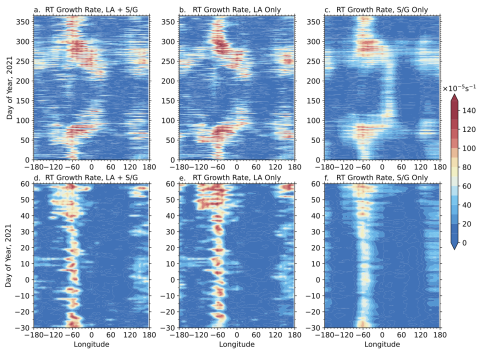
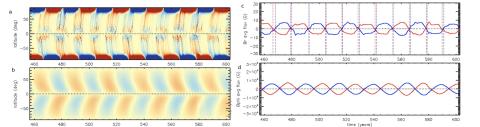
New Expression of the Field-line Integrated Rayleigh-Taylor Instability Growth Rate
Chun-Yen Huang, Tzu-Wei Fang, Arthur Richmond, Timothy Fuller-Rowell, Jenn-Yenq Liu research expressions of newly established Rayleigh-Taylor (R-T) instability growth rates, then perform calculations using the thermospheric and ionospheric conditions based on the coupled Whole Atmosphere Model and Ionosphere Plasmasphere Electrodynamic model (WAM-IPE). The parameters used in this calculation include the field-line integrated conductivities and currents, which consider the Quasi-Dipole Coordinates and the modifications to the equations of electrodynamics.
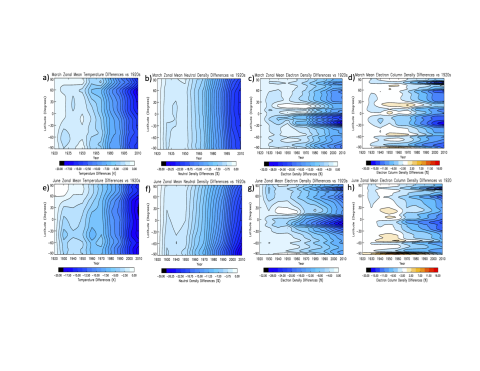
Climate Change in the Thermosphere and Ionosphere From the Early Twentieth Century to Early Twenty‐First Century Simulated by the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model—eXtended
Authors Joseph McInerney, Liying Qian, Han-Li Liu, Stanley Solomon, and Susan Nossal decided to apply the WACCM-X climate model to the upper atmosphere for the decades from the 1920s to 2010s. This type of modeling application will be useful to predict what will happen in the century ahead as greenhouse gases increase and humans make efforts to reverse the increase.
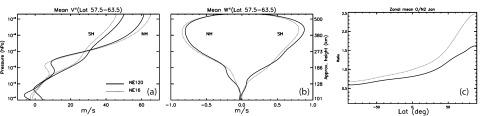
Impacts of gravity waves on the thermospheric circulation and composition
Hanli Liu, Peter Lauritzen, and Francis Vitt use the high-resolution whole atmosphere model to study small-scale wave propagation from the lower atmosphere into the thermosphere. Using this high-resolution model, which can partially resolve the small-scale waves, they can directly quantify the force exerted by these waves on the general circulation in the thermosphere.